Radhe Radhe, B.Pharm students! In this post, you will find the notes for your 3rd semester Physical Pharmaceutics 1 subject . Here you will find notes, books, previous year questions (PYQs), and important question-answers related to your pharmacy course. You will also find GPAT updates here. You will find pharmacy-related vacancies here, so stay calm and connected with Pulse by Anubhav. Join Our Telegram Channel As Well As Bookmark Our Site For Latest Stuff.

As you may have realized, pursuing a B.Pharm degree is not easy. Many people initially choose it as just one option, but later they discover how much studying is involved. Your B.Pharm course is divided into 8 semesters. In the third semester, you have to study a total of 4 subjects, of which all are compulsory. You won’t have to study any additional subjects this semester. You will meet new friends in this semester. There will be lateral entry for D.Pharma students in your class in this semester.
The pharmacy field is a very important medical field. Here, pharmacists not only dispense medication to patients but also educate them about the medicines. In the pharmaceutical industry, these same pharmacists manufacture the medicines and conduct research on them.
The link to download notes for all units is given below. If you want to download the PDF without reading the post, you can download the PDF by clicking on the link given below. You can also join our Telegram channel for future updates.
Also Read- Birthday Girl Jennie – South Korean Singer & BLACKPINK Star
The Subjects in the 3rd semester of B.Pharm are:
- Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry -2
- Pharmaceutical Microbiology
- Physical Pharmaceutics -1
- Pharmaceutical Engineering
Physical Pharmaceutics 1 will be taught to you in the 3rd semester, where you will learn about the substances used in the pharmaceutical industry.
1️⃣ Principles of drug solubility, diffusion, solutions and distribution laws + states of matter and physicochemical properties of drugs are understood.
2️⃣ Surface phenomena, complexation, and protein binding explain drug behavior and stability.
3️⃣ pH, buffers, and isotonic solutions are essential concepts for pharmaceutical and biological systems.
B.Pharm 3rd Semester Physical Pharmaceutics 1 Syllabus
Before downloading the notes, please take a look at the Physical Pharmaceutics 1 syllabus to understand what topics are covered.
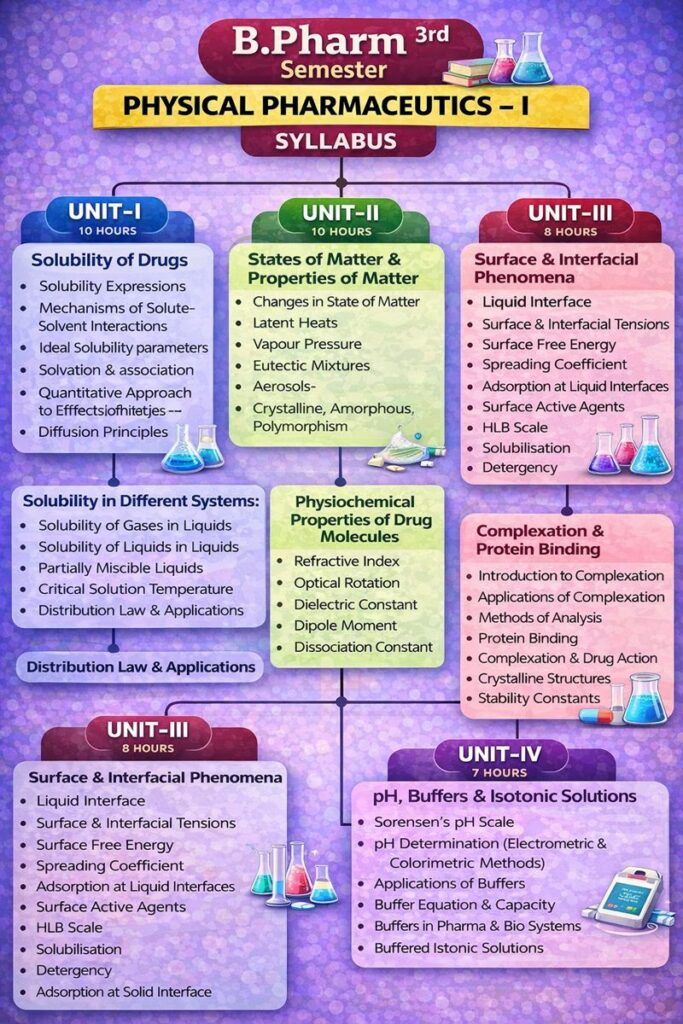
UNIT – I
Solubility of Drugs
- Solubility expressions
- Mechanisms of solute–solvent interactions
- Ideal solubility parameters
- Solvation and association
- Quantitative approach to factors influencing solubility of drugs
- Diffusion principles in biological systems
Solubility in different systems:
- Solubility of gases in liquids
- Solubility of liquids in liquids
- Binary solutions
- Ideal solutions
- Raoult’s law
- Real solutions
- Partially miscible liquids
- Critical solution temperature and applications
- Distribution law, its limitations and applications
UNIT – II
A. States of Matter and Properties of Matter
- States of matter
- Changes in state of matter
- Latent heats
- Vapour pressure
- Sublimation
- Critical point
- Eutectic mixtures
- Gases
- Aerosols – inhalers
- Relative humidity
- Liquid complexes
- Liquid crystals
- Glassy states
- Solids:
- Crystalline
- Amorphous
- Polymorphism
B. Physicochemical Properties of Drug Molecules
- Refractive index
- Optical rotation
- Dielectric constant
- Dipole moment
- Dissociation constant
- Determinations and applications
UNIT – III
Surface and Interfacial Phenomena
- Liquid interface
- Surface & interfacial tensions
- Surface free energy
- Measurement of surface & interfacial tensions
- Spreading coefficient
- Adsorption at liquid interfaces
- Surface active agents
- HLB scale
- Solubilisation
- Detergency
- Adsorption at solid interface
UNIT – IV
Complexation and Protein Binding
- Introduction to complexation
- Classification of complexation
- Applications of complexation
- Methods of analysis
- Protein binding
- Complexation and drug action
- Crystalline structures of complexes
- Thermodynamic treatment of stability constants
UNIT – V
pH, Buffers and Isotonic Solutions
- Sorensen’s pH scale
- pH determination:
- Electrometric method
- Colorimetric method
- Applications of buffers
- Buffer equation
- Buffer capacity
- Buffers in pharmaceutical and biological systems
- Buffered isotonic solutions
Also Read- Understanding Virginity and Its Connection to Rape Cases
B.Pharm 3rd Semester Physical Pharmaceutics 1 Notes PDF
🧪 Download B.Pharm 3rd Semester – Physical Pharmaceutics-I Notes (Unit-wise | Flowchart PDF)
⚡ All Physical Pharmaceutics-I notes are prepared in **simple flowchart format** for quick revision & exams.
🚀 Join Pulse Pharma Notes Telegram Channel 📘 Download Complete Physical Pharmaceutics-I Flowchart Notes PackageAlso Read:- B.Pharm 3rd Semester Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry -2 Notes
B.Pharm 3rd Semester Physical Pharmaceutics 1 Book PDF
Books are very important; you should definitely check out the books according to your syllabus. During your pharmacy studies, books from Nirali Prakashan and PV Sindhu are very helpful. You can download the PDFs from the link below.
- Pharmaceutical Physical Pharmaceutics 1 Nirali Prakashan Full Book PDF:- PDF
- Pharmaceutical Physical Pharmaceutics 1 Chemistry PV Sindhu Full Book PDF:- PDF
- Pharmaceutical Physical Pharmaceutics 1 Chemistry Thakur Publication Full Book PDF:- PDF
- Pharmaceutical Physical Pharmaceutics 1 Chemistry The Point Publication Full Book PDF: PDF
❓ Physical Pharmaceutics–I (PP-I) – FAQs
What is Physical Pharmaceutics–I?
PP-I is a core B.Pharm 3rd semester subject that explains drug solubility, diffusion, states of matter, surface phenomena, complexation, and pH–buffers with pharmaceutical and biological applications.
Which unit is most important in PP-I?
UNIT I (Solubility & Distribution law) and UNIT V (pH & Buffers) are most frequently asked in university exams and have high practical relevance.
Why is Solubility (UNIT I) important?
Solubility governs drug absorption, bioavailability, diffusion in biological systems, and helps in formulation design of medicines.
What is the key focus of UNIT III?
UNIT III focuses on surface & interfacial tension, adsorption, surfactants, HLB scale, solubilisation, and detergency in pharmaceutical systems.
Why are pH and Buffers (UNIT V) crucial?
Buffers maintain drug stability, control pH of formulations, and help prepare buffered isotonic solutions for safe biological use.
B.Pharm 3rd Semester Notes
| Subject Name | Notes Link |
|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry – II Notes | View Notes |
| Pharmaceutical Microbiology Notes | View Notes |
| Physical Pharmaceutics – I Notes | View Notes |
| Pharmaceutical Engineering Notes | View Notes |
2 thoughts on “B.Pharm 3rd Semester Physical Pharmaceutics 1 Notes”