Radhe Radhe, B.Pharm students! In this post, you will find the notes for your 4th semester Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry – 3 subject . Here you will find notes, books, previous year questions (PYQs), and important question-answers related to your pharmacy course Syllabus. You will also find GPAT updates here. Here You will find pharmacy-related vacancies, so stay calm and connected with Pulse by Anubhav. Join Our Telegram Channel As Well As Bookmark Our Site For Latest Stuff.

As you may have realized, pursuing a B.Pharm degree is not easy. Many people initially choose it as just one option, but later they discover how much studying is involved. Your B.Pharm course is divided into 8 semesters. In the fourth semester, you have to study a total number of 5 subjects, of which all are compulsory. You won’t have to study any additional subjects in this semester.
The pharmacy field is a very important medical field. Here, pharmacists not only dispense medication to patients but also educate them about the medicines. In the pharmaceutical industry, these same pharmacists manufacture the medicines and conduct research on them.
The link to download notes for all units is given below. If you want to download the PDF without reading the post, you can download the PDF by clicking on the link given below. You can also join our Telegram channel for future updates.
Also Read- From Taskaree’s ‘Priya’ to Bollywood: Zoya Afroz’s bold avatar is surprising everyone.
The Subjects in the 4th semester of B.Pharm are:
- Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry – 3
- Physical Pharmaceutics – 2
- Medicinal Chemistry – 1
- Pharmacology – 1
- Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry – 1
Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry – 3 is a subject you will study in your 4th semester of the 2nd year, where you will learn about various chemical reactions. This subject is related to Organic Chemistry 2. You will also need to focus on the previous syllabus.
B.Pharm 4th Semester Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry – 3 Syllabus
Before downloading the notes, please take a look at the Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry – 3 syllabus to understand what topics are covered.
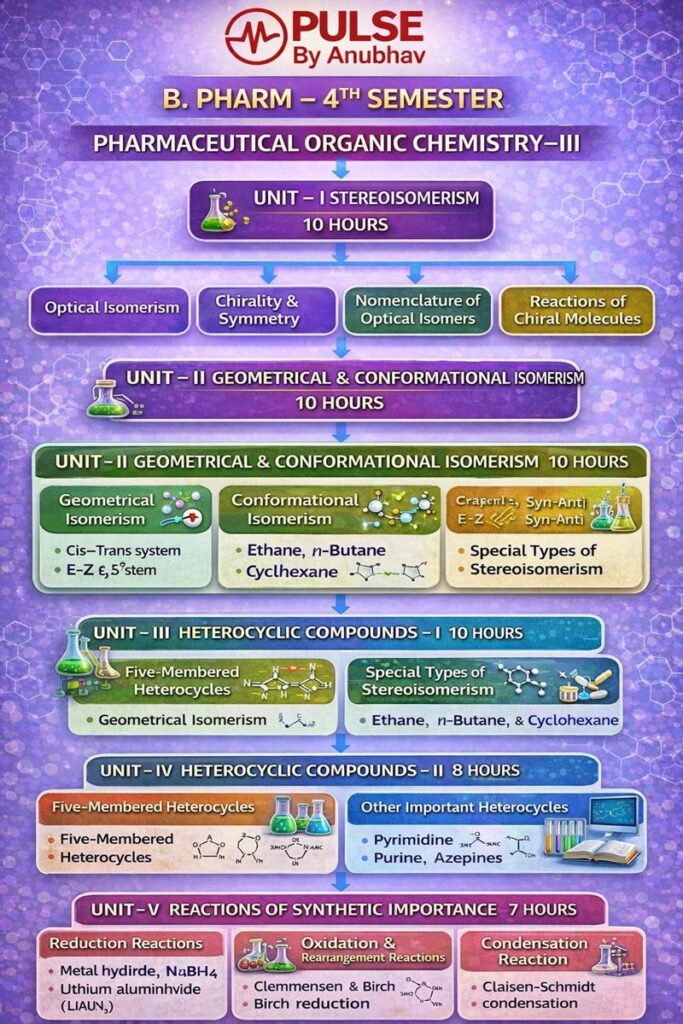
UNIT – I : Stereoisomerism
Optical Isomerism
- Optical activity
- Enantiomerism
- Diastereoisomerism
- Meso compounds
Chirality & Symmetry
- Elements of symmetry
- Chiral and achiral molecules
Nomenclature of Optical Isomers
- D–L system of nomenclature
- Sequence rules
- R–S system of nomenclature
Reactions of Chiral Molecules
- Racemic modification
- Resolution of racemic mixture
Asymmetric Synthesis
- Partial asymmetric synthesis
- Absolute asymmetric synthesis
UNIT – II : Geometrical & Conformational Isomerism
Geometrical Isomerism
- Nomenclature of geometrical isomers:
- Cis–Trans system
- E–Z system
- Syn–Anti system
- Methods for determination of configuration of geometrical isomers
Conformational Isomerism
- Ethane
- n-Butane
- Cyclohexane
Special Types of Stereoisomerism
- Stereoisomerism in biphenyl compounds (Atropisomerism)
- Conditions for optical activity
Stereochemical Reactions
- Stereospecific reactions
- Stereoselective reactions
UNIT – III : Heterocyclic Compounds – I
General Introduction
- Nomenclature and classification of heterocyclic compounds
Five-Membered Heterocycles
- Pyrrole
- Furan
- Thiophene
Study Includes
- Synthesis
- Reactions
- Medicinal uses
Comparative Study
- Relative aromaticity
- Reactivity of Pyrrole, Furan and Thiophene
UNIT – IV : Heterocyclic Compounds – II
Five-Membered Heterocycles
- Pyrazole
- Imidazole
- Oxazole
- Thiazole
(Synthesis, reactions and medicinal uses)
Six-Membered & Fused Heterocycles
- Pyridine (basicity of pyridine)
- Quinoline
- Isoquinoline
- Acridine
- Indole
Other Important Heterocycles
- Pyrimidine
- Purine
- Azepines
(Synthesis and medicinal uses)
UNIT – V : Reactions of Synthetic Importance
Reduction Reactions
- Metal hydride reduction:
- Sodium borohydride (NaBH₄)
- Lithium aluminium hydride (LiAlH₄)
- Clemmensen reduction
- Birch reduction
- Wolff–Kishner reduction
Oxidation & Rearrangement Reactions
- Oppenauer oxidation
- Dakin reaction
- Beckmann rearrangement
- Schmidt rearrangement
Condensation Reaction
- Claisen–Schmidt condensation
Also Read- Understanding Virginity and Its Connection to Rape Cases
B.Pharm 4th Semester Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry – 3 Notes PDF
🧪 Download B.Pharm 4th Semester – Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry-III Notes (Unit-wise | Flowchart PDF)
⚡ Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry-III notes are prepared in **easy flowchart format** for quick revision, strong concepts & university exams.
🚀 Join Pulse Pharma Notes Telegram Channel 📘 Download Complete Organic Chemistry-III Flowchart NotesAlso Read:- B.Pharm 3rd Semester Pharmaceutical Engineering Notes
B.Pharm 4th Semester Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry – 3 Book PDF
Books are very important; you should definitely check out the books according to your syllabus. During your pharmacy studies, books from Nirali Prakashan and PV Sindhu are very helpful. You can download the PDFs from the link below.
- Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry – 3 Nirali Prakashan Full Book PDF:- PDF
- Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry – 3 Chemistry PV Sindhu Full Book PDF:- PDF
- Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry – 3 Chemistry Thakur Publication Full Book PDF:- PDF
- Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry – 3 Chemistry The Point Publication Full Book PDF: PDF
❓ Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry-III – Frequently Asked Questions (B.Pharm 4th Semester)
What is Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry-III?
Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry-III deals with stereochemistry, heterocyclic compounds and important organic reactions used in drug synthesis and pharmaceutical applications.
Which unit is most important in Organic Chemistry-III?
UNIT I (Stereoisomerism) and UNIT II (Geometrical & Conformational Isomerism) are highly important and frequently asked in university examinations.
Why is stereoisomerism important in pharmaceuticals?
Stereoisomerism affects biological activity, potency and safety of drugs. Enantiomers of the same drug can show different pharmacological actions.
What is the significance of R-S and D-L nomenclature?
R-S and D-L systems help in identifying the spatial arrangement of atoms in chiral molecules, which is crucial for understanding drug activity and synthesis.
Why are heterocyclic compounds important in pharmacy?
Most drugs contain heterocyclic rings. Compounds like pyridine, imidazole, indole and purine show wide medicinal uses including antibacterial, antifungal and anticancer activity.
Which heterocyclic compounds are covered in this subject?
Pyrrole, furan, thiophene, pyrazole, imidazole, oxazole, thiazole, pyridine, quinoline, isoquinoline, indole, pyrimidine and purine.
Why are name reactions important in Organic Chemistry-III?
Name reactions like Clemmensen, Birch, Wolff-Kishner and Beckmann rearrangement are essential for synthesis of pharmaceutical intermediates and exam scoring.
How to score well in Organic Chemistry-III exams?
Focus on reaction mechanisms, stereochemical concepts, flowcharts, structures and medicinal uses of heterocyclic compounds for high scoring answers.
B.Pharm 4th Semester Notes
| Subject Name | Notes Link |
|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry – III Notes | View Notes |
| Pharmaceutical Physical Pharmaceutics – II Notes | View Notes |
| Pharmaceutical Medicinal Chemistry – I Notes | View Notes |
| Pharmaceutical Pharmacology – I Notes | View Notes |
| Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry – I Notes | View Notes |
3 thoughts on “B.Pharm 4th Semester Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry – 3 Notes”